Figure 5. There is a dissociation between colocalization of VGLUT3 and 5-HT in cell bodies vs. axons.
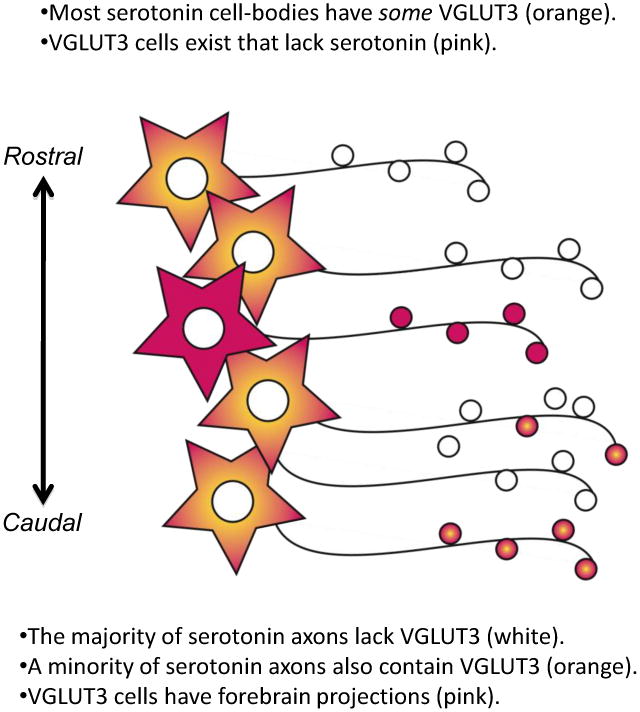
Many 5-HT cell bodies have some detectable VGLUT3-immunolabeling (orange), whereas the majority of 5-HT axons in the forebrain lack detectable VGLUT3-immunolabeling (white). Axons containing both VGLUT3 and 5-HT (orange boutons) vary in abundance by brain region. Several areas richly invested with axons containing both VGLUT3 and 5-HT are projection sites of the caudal DR. In addition, there are many VGLUT3 containing cells in the DR that lack 5-HT (pink). These “VGLUT3-glutamate cells” also contribute to ascending projections from the DR (pink). Thus, axons arising from the DR contain 5-HT, VGLUT3, or a combination of both together.
