Figure 7. Schematic representation of network interactions of VGLUT3-glutamate cells and 5-HT neurons.
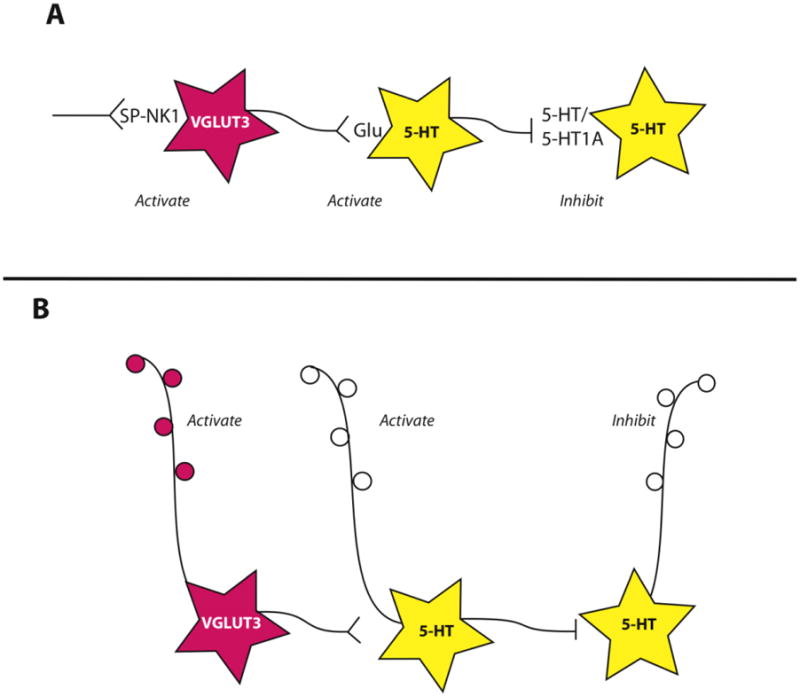
see text for references. A. Substance P (SP) acting at its receptor, neurokinin 1 (NK1) has the capacity to activate VGLUT3-glutamate neurons (pink). These neurons in turn release glutamate onto some 5-HT neurons (yellow), driving their activation and 5-HT release. This subsequently triggers inhibition of other serotonin neurons via 5-HT1A receptors. This scheme explains experimental observations in the rostral and middle portion of the DR, different relationships may exist in the caudal DR. B. VGLUT3-glutamate neurons also contribute to output projections of the DR, raising the possibility of reciprocal activation states between different output pathways.
