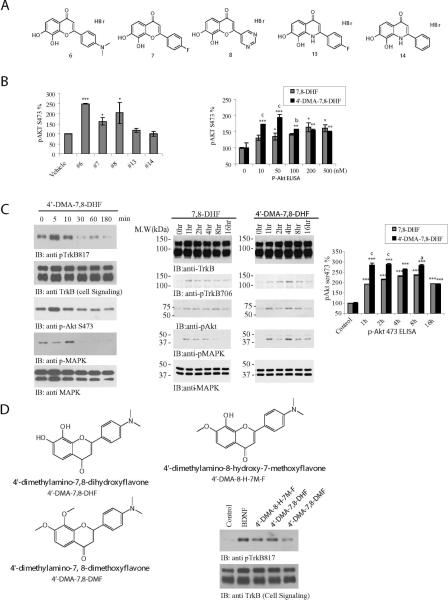
Figure 3. 4'-dimethylamino-7,8-dihydroxyflavone displays more potent TrkB stimulatory effect than parental 7,8-dihydroxyflavone.
(A) Chemical structures of various 7,8-DHF derivatives. (B) Phospho-Akt ELISA assay by the synthetic compounds in cortical neurons. Primary cortical cultures from E17 rat embryos were treated with 500 nM of various 7,8-DHF derivatives. The cell lysates were analyzed by the ELISA (left panel) (*: P<0.05, ***: P<0.001 vs vehicle, Student's t-test). Different doses of 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF and 7,8-DHF were incubated with primary cortical neurons for 15 min. The cell lysates (20 μg) were analyzed with p-Akt ELISA (right panel) (*: P<0.05, **: P<0.01, ***: P<0.001 vs control, one-way ANOVA; b: P<0.01, c: P<0.001 vs 7,8-DHF at same concentration, Student's t-test). The data were from 2 sets of replicated experiments (mean ± SEM). (C) Time course assay with 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF. Rat primary neurons were treated with 500 nM 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF fro various time points. The neuronal lysates were analyzed with various antibodies. 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF rapidly activated TrkB and its downstream signaling cascades (left panels). 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF revealed longer period of TrkB activation in mouse brain. 1 mg/kg of 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF and 7,8-DHF were orally administrated into C57 BL/6J mice and TrkB phosphorylation and its downstream signaling cascades including Akt and MAPK in mouse brain were analyzed by immunoblotting at various time points. TrkB activation by 4'-DMA-7,8-DHF peaked at 4 h, whereas the maximal TrkB activation by 7,8-DHF in mouse brain occurred at 1–2 h (middle panels). P-Akt 4734 ELISA in drug treated mouse brain was analyzed (right panel) (***: P<0.001 vs control, one-way ANOVA; a: P<0.05, c: P<0.001 vs 7,8-DHF at same concentration, Student's t-test). The data were from 2 sets of replicated experiments (mean ± SEM). (D) 7,8-dihydroxy groups are essential for the flavone's agonistic effect. Different methoxy replaced derivatives were tested on primary neurons by immunoblotting assays.