Fig. 4.
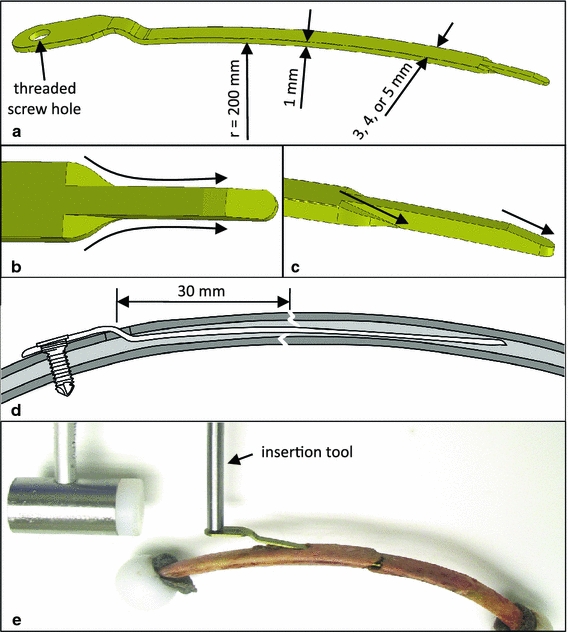
a The rib splints have an intramedullary shaft with a rectangular cross-section to provide rotational stability and cut-out resistance, while maintaining flexible fixation; b, c the tapered and sloped splint tip facilitates insertion and guides the splint along the intramedullary canal; d the rib splints are inserted through an entry portal at a distance of 30 mm from the fracture, and are secured with a locking screw to prevent splint migration; e the splints are inserted with a custom tool that can be rigidly connected to the splint
