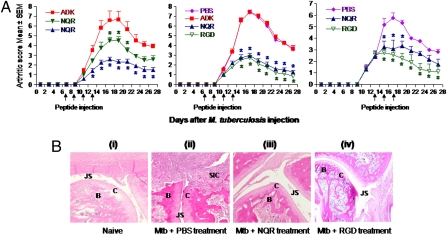
Fig. 3.
Treatment of arthritic Lewis rats with the phage-encoded peptides suppresses adjuvant arthritis. (A) Group of arthritic Lewis rats (n = 4 per group) were injected with a peptide (ADK, NQR, or RGD) or PBS i.v. on the days indicated by the arrows either at the onset or just after the onset of arthritis. The rats were monitored regularly for the disease severity, presented as “arthritic score.” (Left) The difference between NQR (filled inverted triangle; 1 mg/kg) and ADK was significant (*P < 0.05) from day 17 to day 21, as was the difference between NQR (filled triangle; 2 mg/kg) and ADK from day 13 to day 26. (Center) The difference between NQR/RGD and PBS/ADK was significant from day 15 to day 27. (Right) The difference between NQR and PBS was significant from day 15 to day 19, whereas that between RGD and PBS was significant from day 15 to day 27. In all three panels, the differences between other groups not specified above were not significant. Similar results were obtained in repeat experiments. (B) Representative H&E-stained hind paw sections of a naïve rat (i), an arthritic rat treated with PBS instead of peptide (ii), an arthritic rat treated with NQR peptide (iii), and an arthritic rat treated with RGD peptide (iv) are shown. The sections were graded for histopathological features associated with arthritis. B, bone; C, cartilage; JS, joint space; SIC, synovium-infiltrating cells.