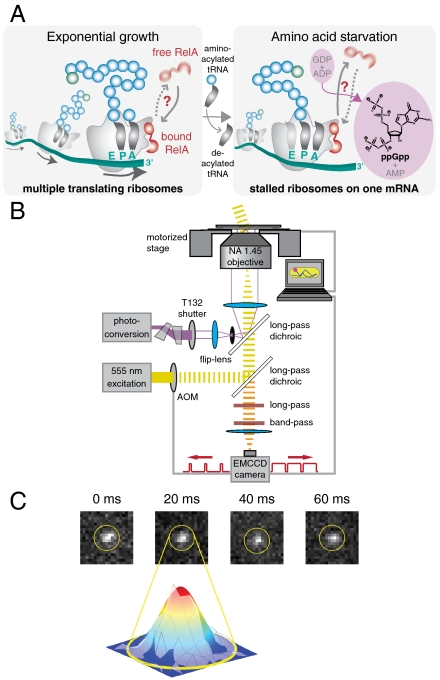
Fig. 1.
Single-molecule tracking in living cells. (A) Schematic drawing of RelA interacting with a polysome. During exponential cell growth, RelA could either be bound to the polysome (10) or diffuse rapidly in the cytosol (Left). During amino acid limitation the level of tRNA acylation drops, resulting in accumulation of deacylated tRNA in the ribosomal A site. Under these conditions RelA could either be in tight complex with a polysome (46) or unbind from the ribosome and undergo rapid cytosolic diffusion (Right). (B) Schematic diagram of the optical setup. An acousto-optical modulator is synchronized with an EMCCD camera and shutters a wide-field yellow excitation laser beam to pass short excitation pulses in the middle of each imaging frame. A violet photoconversion laser beam is spatially overlapped and can either be focused onto the back aperture of an Olympus TIRF objective or focused onto the sample plane via a flip-lens. (C) Four consecutive frames of a time-lapse movie of RelA–Dendra2 (in nonstarved cells) with a frame time of 20 ms and an exposure time of 5 ms and a Gaussian fit to frame 2.