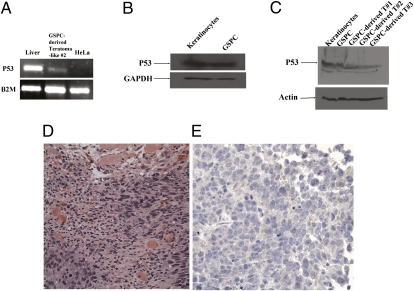
Fig. 7.
In vivo characterization of GSPCs in the SCID mouse. (A) p53 mRNA was detected in the GSPC-derived immature teratoma-like cell masses. Total RNA from liver cells, teratoma-like GSPCs, and HeLa cells was extracted and converted into cDNA. p53 was detected in liver cells and teratoma-like GSPCs but not in HeLa cells. This result indicates that GSPCs expresses p53, whereas the cancer cell line HeLa does not express p53 at the mRNA level. (B) Western blot analyses indicate that p53 protein was detected in both keratinocytes and GSPCs. Cells were grown as described in Materials and Methods, and the lysate proteins were subjected to SDS/PAGE. The samples were subjected to immunoblot analyses as described in Materials and Methods. Equivalent amounts of total cell lysates were loaded to all the lanes. Note that anti-p53 mAb specifically binds to p53 protein, whereas anti-GAPDH antibody specifically recognizes GAPDH. These results further demonstrate that p53 is present at the protein level. (C) Western blot analyses show that p53 protein was detected in the GSPC-derived immature teratoma-like cell masses. Equivalent amounts of total cell lysates were loaded to all the lanes. Note that anti-p53 mAb specifically binds to p53 protein, whereas anti-α-actin antibody specifically recognizes α-actin. These results further demonstrate that p53 is present at the protein level. (D) Immature epithelial cells grow in solid nests in the right and left lower corners of this image. These cells are larger than the surrounding mature stromal cells (mostly fibroblasts and scattered groups of endothelial cells), with increased nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratios and prominent nucleoli. Mitosis is present in the left lower corner within the area of the immature epithelial cells, suggesting rapid growth of the cells. Areas of necrosis (not shown) were appreciated. Foci of degenerated skeletal muscle cells with abundant pink cytoplasm are present in the center and upper portion of the image (H&E stain). (Magnification: 40×.) (E) Weak cytoplasmic positive staining of the immature epithelial cells with S-100, a neural marker, is observed, suggesting neural differentiation of these cells. (Magnification: 40×.)