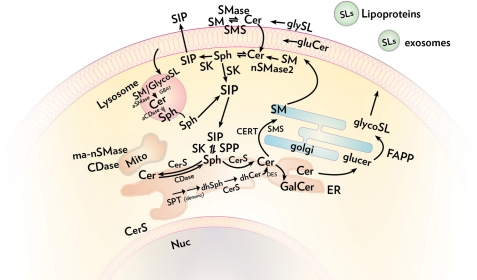
FIGURE 2.
Compartmentalization of sphingolipid metabolism. Ceramide (Cer) is synthesized de novo in the ER and then is transported either via ceramide transfer protein (CERT) to the Golgi, where it serves as a substrate for the synthesis of sphingomyelin (SM), or is transported by vesicular traffic for the synthesis of glucosylceramide (gluCer) (97). Sphingomyelin and glycosphingolipids (GlycoSL) are, in turn, transported to the plasma membrane through vesicular trafficking, and they also undergo vesicular trafficking in the endosomal system and clearance through lysosomal degradation. Ceramide can also be transformed to galactosylceramide (GalCer) in the ER, a process enriched in neural tissues. SLs, sphingolipids; SMS, sphingomyelin synthase; glySL, glycosphingolipids; dhSph, dihydrosphingosine; aCDase, acid ceramidase; ma-nSMase, mitochondrial associated SMase; aSMase, acid SMase; SK, sphingosine kinase; Sph, sphingosine; CDase, ceramidase; dhCer, dihydroceramide; Mito, mitochondria; Nuc, nucleus.