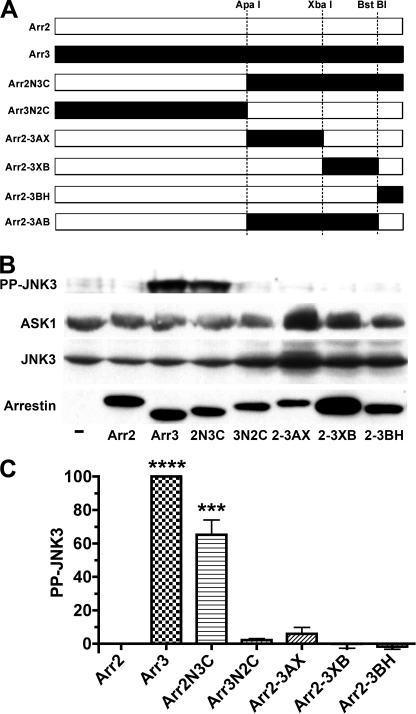
FIGURE 1.
Arrestin ability to activate JNK3 is largely determined by the C-terminal domain. A, schematic of the arrestin-2/3 chimeras, with arrestin-2- and arrestin-3-derived elements shown in white and black, respectively. The positions of the restriction sites engineered in homologous places in coding sequences and used to swap elements are indicated. Arr2, arrestin-2; Arr3, arrestin-3. Arr2N3C is a chimera with the N-terminal domain (residues 1–180) of arrestin-2 and the C-terminal domain (residues 182–408) of arrestin-3. Arr3N2C is the reverse chimera with the N- and C-terminal domains of arrestin-3 and arrestin-2, respectively. Arr2-3AX is arrestin-2 with the arrestin-3 element between the ApaI and XbaI sites (residues 182–290). Arr2-3XB is arrestin-2 with the arrestin-3 element between the XbaI and BstBI sites (residues 291–389). Arr2-3BH is arrestin-2 with the arrestin-3 element downstream of the BstBI site (residues 390–408). Arr2-3AB is arrestin-2 with the arrestin-3 element between the ApaI and BstBI sites (residues 182–389). B, COS-7 cells were transfected with HA-ASK1, HA-JNK3, and the indicated arrestins with a C-terminal FLAG tag; harvested 48 h post-transfection; and lysed. The amount of active phosphorylated JNK3 (PP-JNK3; upper blot) and the expression of ASK1, JNK3, and arrestins were determined by Western blotting. C, quantification of the level of JNK3 phosphorylation in cells expressing the indicated arrestins. Phosphorylated JNK3 bands from three to four independent experiments were quantified. The data were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with arrestin as a main factor, followed by the Bonferroni-Dunn post-hoc test. The significance of the difference from arrestin-2 is shown. ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Band intensity is expressed as a percent of the difference between phosphorylated JNK3 in arrestin-3- and arrestin-2-expressing cells.