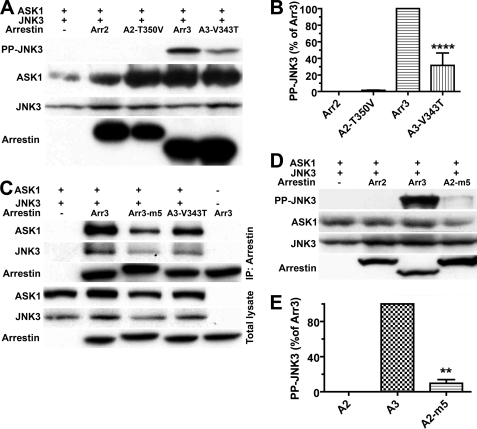
FIGURE 6.
A single substitution significantly reduces the activity of arrestin-3, but even multiple substitutions do not bring the activity of arrestin-2 to the level of arrestin-3. A and D, COS-7 cells expressing HA-ASK1, HA-JNK3, and the indicated arrestins with a C-terminal FLAG tag were lysed, and the amount of active phosphorylated JNK3 (PP-JNK3; upper blot) and the expression of ASK1, JNK3, and arrestins were determined by Western blotting. B and E, quantification of the level of JNK3 phosphorylation in cells expressing the indicated arrestins. Phosphorylated JNK3 bands from three independent experiments were quantified. The data were analyzed by ANOVA with arrestin as a main factor, followed by the Bonferroni-Dunn post-hoc test. The significance of the difference from fully active arrestin-3 (Arr3, A3; B) or from inactive arrestin-2 (A2; E) is shown; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001. Band intensity is expressed as a percent of the difference between phosphorylated JNK3 in arrestin-3- and arrestin-2-expressing cells. C, COS-7 cells were transfected with the indicated proteins and lysed 48 h post-transfection. Arrestins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody, and the amount of arrestins and co-immunoprecipitated HA-ASK1 and HA-JNK3 was determined by Western blotting (upper three blots). The expression of these proteins was determined in cell lysates (lower three blots). Cells transfected with HA-ASK1 + HA-JNK3 only (first lane) or arrestin only (last lane) served as controls. The results of a representative experiment of three performed are shown.