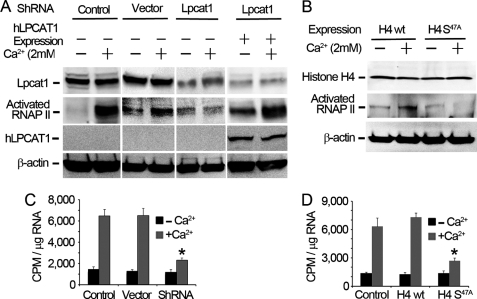
FIGURE 5.
Histone H4 palmitoylation regulates global RNA synthesis. A, MLE cells were transfected with empty vector or Lpcat1 shRNA plasmids for 48 h, followed by exposure of cells to the presence or absence of 2 mm Ca2+. For rescue, one group of cells was first transfected with Lpcat1 shRNA for 48 h prior to overexpression with human Lpcat1 (hLpcat1) for another 24 h. Cell lysates were subject to Lpcat1, RNA polymerase II, and β-actin immunoblot analysis. B, wild type histone H4 and histone H4 S47A mutant plasmids expressing a COOH-terminal V5 tag were ectopically expressed in MLE cells, and after 24 h, cells were treated with or without 2 mm Ca2+. Cell lysates were then processed for V5, RNA polymerase II, and β-actin immunoblot analysis. C and D, MLE cells in A or B were pulse-chase-labeled with [32P]UTP for 2 h in the presence or absence of 2 mm Ca2+, total RNA was extracted using the TRIzol method, and the radioactivity of the isolated RNA was measured by scintillation counting. The data represent three independent experiments. C, p = 0.0015, radioactivity in Ca2+-treated shRNA versus Ca2+-treated wild type; D, p = 0.0004, radioactivity in Ca2+-treated H4 S47A mutation versus Ca2+-treated wild type H4. Error bars, S.E.