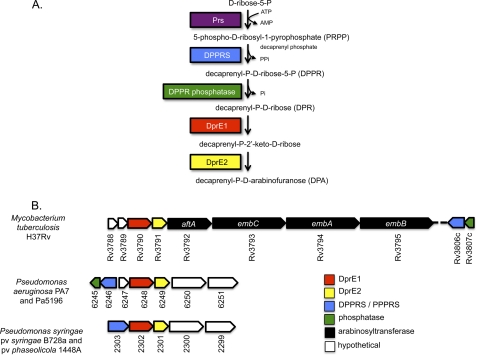
FIGURE 1.
d-Arabinofuranose biosynthesis in P. aeruginosa. A, proposed pathway of d-Araf biosynthesis based on studies in the Corynebacterineae. Phospho-d-ribose pyrophosphate, the first intermediate of the pathway, is likely generated by Prs, a common enzyme involved in bacterial purine metabolism. In PA7, Prs is encoded by PsPA7_5320. B, genes involved in d-Araf biosynthesis in Mycobacterium and Pseudomonas. Open reading frames encoding the enzymes that are predicted to generate the intermediates shown in A are shown in matching colors. Genes are numbered according to the H37Rv, PA7, and B728a genome designations with the strain prefixes eliminated for clarity and are not drawn to scale. DPPRS, decaprenyl-P-ribose-5-P synthetase; PPPRS, polyprenyl-P-ribose-5-P synthetase.