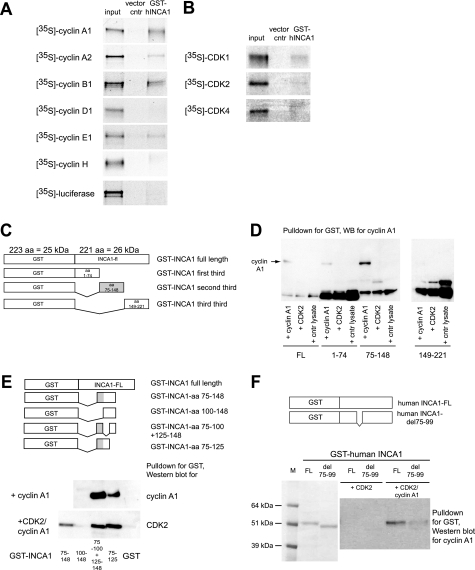
FIGURE 1.
GST-pulldown assays revealed a cyclin A1-binding site at amino acids 75–99 in the human INCA1 protein. A, GST pulldown assays using 35S-labeled cyclins and GST-INCA1 were performed to identify INCA1-binding cyclins. INCA1 interacted directly with the CDK2-specific cyclins A1, A2, B1, and E1 but not with cyclin D1 or H. B, GST pulldown assays as in A revealed only weak binding of GST-INCA1 to CDKs. C, constructs used to determine cyclin-CDK-binding sites in initial experiments. Because the domain structure of INCA1 is unknown, three different deletion mutants were generated and tested. The gray box indicates the binding site. aa, amino acids. D, cyclin A1 bound to amino acids 75–148 of human INCA1. The weak band in this blot at amino acids 1–74 was not consistently reproducible. No binding to amino acids 149–221 was observed. The lower bands are nonspecific. WB, Western blot. E, upper panel, further GST-INCA1 deletions were constructed to localize the region responsible for CDK and cyclin binding. The gray box indicates the binding site. Lower panel, pulldown assays using further deletion mutants indicate that amino acids at positions 75–99 of INCA1 are required and sufficient for binding of cyclin A1 and CDK2. F, amino acids 75–99 that are required for cyclin-CDK binding were deleted in the full-length construct (upper panel). Coomassie staining of the proteins expressed in E. coli from the constructs to determine the equal amounts of both proteins for the pulldown assays depicted (lower panel, left side). Upon incubation with CDK2 and cyclin A1, the INCA1 deletion mutant del75–99 showed strongly decreased binding affinity for cyclin A1 (lower panel, right side). M, marker; FL, full-length INCA1; del 75–99, deletion mutant of full-length INCA1 lacking amino acids 75–99.