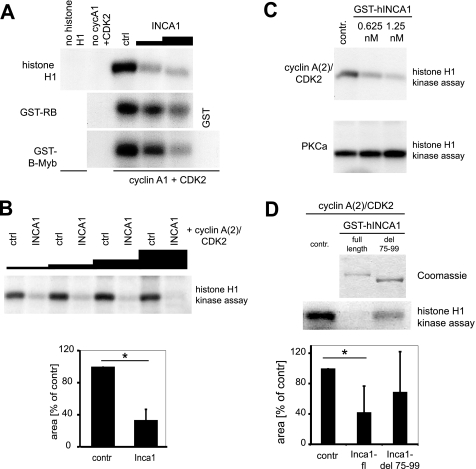
FIGURE 2.
INCA1 inhibits CDK activity in vitro. A, INCA1 dose-dependently inhibited CDK phosphorylation of histone H1, GST-Rb, GST-B-Myb. Baculovirally infected Sf9 cells expressing cyclin A1/CDK2 were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP and different CDK substrates and analyzed by autoradiography. No signals were detected without substrates (no histone H1 or GST alone) or in the absence of cyclin A1/CDK2. ctrl, control. B, upper panel, histone H1 kinase assays using different amounts of lysates from High5 insect cells infected with a baculovirus expressing INCA1 showed a dose-dependent inhibition of CDK2·cyclinA(2) complex activity compared with lysates from uninfected control cells (ctrl). Lower panel, densitometric analysis indicates the statistical significance of CDK2 inhibition by INCA1 (p < 0.001). C, purified full-length INCA1 inhibited CDK2-dependent kinase activity dose-dependently in the low nanomolar range (upper panel), but the activity of protein kinase Cα was not altered (lower panel). Recombinant and purified CDK2·cyclin A(2) complexes or PKCα were incubated with two concentrations of purified GST-INCA1 and analyzed in histone H1 kinase assays. contr, control. D, upper part, in histone H1 kinase assays, full-length but not the cyclin-binding mutant human INCA1-del 75–99 (see Fig. 1, B–F) inhibited cyclin A2/CDK2 activity. Recombinant and purified CDK2·cyclin A(2)-complexes alone (contr) or in combination with either GST-INCA1-full length (FL) or GST-INCA1-del75–99 were analyzed in histone H1 kinase assays (lower panel). A Coomassie staining confirmed equal expression (upper panel). Lower part, densitometric analysis underlines the significant decreased CDK2 activity upon inhibition by INCA1 (*, p = 0.006), whereas the mutated INCA1 could not significantly inhibit CDK2 (p = 0.23, n.s., not significant).