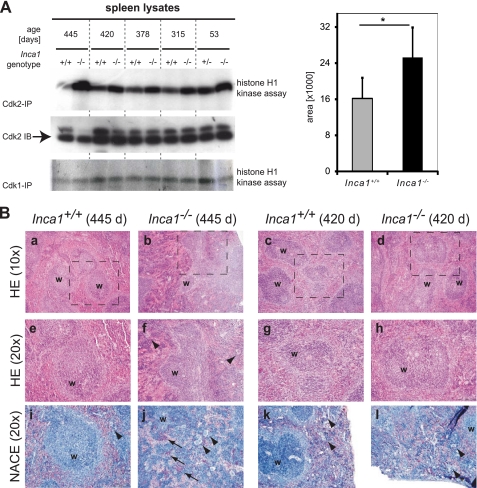
FIGURE 6.
Inca1 is required for Cdk2 inhibition in vivo in the spleen. A, CDK associated kinase activity in Inca1+/+ and Inca1−/− spleens. Cdk2- or Cdk1-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated from lysates of control and Inca1−/− spleens and subjected to histone H1 kinase assays. In the absence of Inca1, Cdk2 activity was consistently increased compared with lysates from wild type animals (upper panel). Cdk1 activity was unchanged (lower panel). Cdk2 Western blot (middle panel) confirmed equal amounts of Cdk2 in the lysates. Densitometric analysis determined that the Cdk2 activity was significantly increased in Inca1−/− compared with the Inca1+/+ spleens (*, right panel; p = 0.035). B, H&E (HE) staining (panels a–h) and naphthol and ASD chloroacetate esterase (NACE) staining of granulopoietic cells (panels i–l). The Inca1-deficient spleen from a 445-day-old mouse showed a disorganized structure of the white pulp (“w” in panels b and f), an increased number of megakaryocytes (arrowheads in panels f and j), and prominent extramedullary hematopoiesis (arrows in panel j hint at red-stained granulocytes). Other spleens also tested in the kinase assays depicted in Fig. 5C were represented by the spleens of the 420-day-old pair of mice, which did not differ significantly concerning their white pulp structure (w in panels c and d, g and h) and the occurrence of megakaryocytes (arrowheads in panels k and l) or extramedullary hematopoiesis, respectively. Marked areas in panels a–d are shown with higher magnifications in panels e–h.