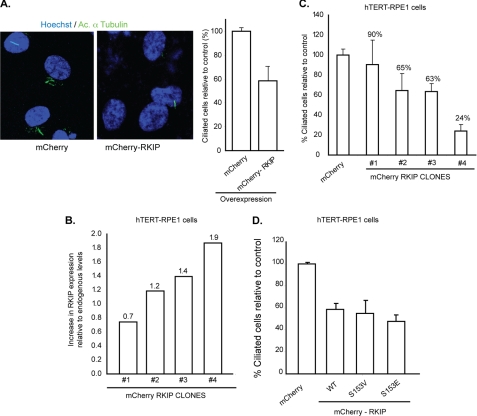
FIGURE 6.
Increased levels of Rkip affect cilia formation in hTERT-RPE1 cells. A, hTERT-RPE1 cells stably expressing mCherry-Rkip or mCherry alone (control) were assessed for cilia growth by immunofluorescence using acetylated (Ac) α-tubulin (green). Histogram shows quantitative analysis of the number of ciliated cells. Data represent mean ± S.D. (p < 0.05). B and C, the levels of mCherry-Rkip were analyzed from four different clones of hTERT-RPE1 cells with stable expression of mCherry-Rkip and a ratio over the level of endogenous Rkip expression was calculated. The different clones were cultured in ciliogenesis conditions (serum starvation) and the number of ciliated cells was assessed by the acetylated α-tubulin immunofluorescence signal. All clones displayed a dose-dependent effect of overexpression of Rkip on ciliogenesis (C). Data represent mean ± S.D. of more than 100 cells analyzed in three independent experiments. D, number of ciliated hTERT-RPE1 cells was assessed after overexpression of mCherry-tagged constitutively phosphorylated (S153E) or non-phosphorylated (S153V) mutants of Rkip. Cilia growth was assessed by acetylated α-tubulin staining. As control, we overexpressed mCherry tag alone. Data represent mean ± S.D. of more than 100 cells analyzed in each group on three independent experiments.