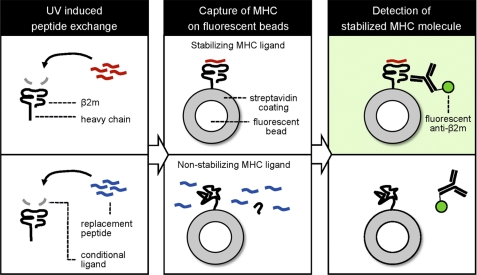
FIGURE 1.
Principle of the MHC stability assay on fluorescent beads. Recombinantly produced MHC molecules loaded with conditional ligands are exposed to UV light resulting in peptide exchange for a binding ligand (red, top row) or nonbinding ligand (blue, bottom row). The emptied MHC molecule is then stabilized and rescued or not stabilized, resulting in its unfolding, respectively. The MHC products are subsequently captured onto streptavidin-coated fluorescent beads, and properly folded complexes can be detected with labeled antibodies that are peptide-specific, MHC conformation-specific, or specific for the noncovalently bound β2m subunit, followed by flow cytometry analysis.