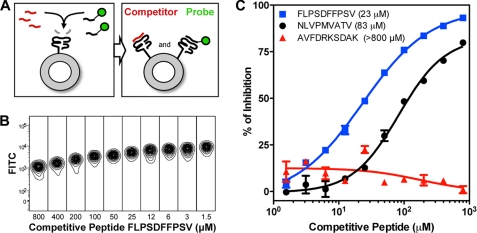
FIGURE 5.
Peptide competition assay. A, the principle of the assay entails peptide competition for the empty peptide-binding site of the MHC molecule after UV cleavage of the conditional ligand. A number of MHC molecules on the bead acquire the probe, whereas other MHC molecules are occupied by the competitor peptide. The final fluorescent signal intensity depends on the concentration of both probe and competitive peptide. B, an increase in FITC fluorescence is observed when the probe FLPSD(Lys-FITC)FPSV competes with the serially diluted competitor peptide P10 for binding HLA-A*02:01 molecules captured on Blue beads. C, plotting the concentration of competitive peptide as a function of the percentage of inhibition allows the determination of IC50 values, as demonstrated for P2 (NLVPMVATV, 83 μm), P10 (FLPSDFFPSV, 23 μm), and P11 (AVFDRKSDAK, >800 μm).