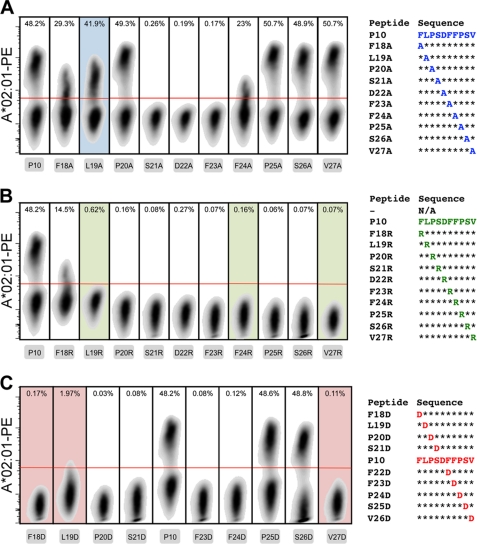
FIGURE 6.
MHC tetramer staining of transduced T cells. Lymphocytes with an hepatitis B virus core 18–27-specific T cell receptor were obtained through transduction and specifically expanded in culture. PE-conjugated HLA-A*02:01 tetramers that were peptide-exchanged with the alanine (A), arginine (B), and aspartic acid (C) derivatives of parent peptide P10 were evaluated for their capability to stain the lymphocytes specifically gating first on the monodisperse (forward and side scatter), viable (near-IR, Live/Dead negative), and CD8+ (anti-CD8 Pacific Blue-positive) cells. The red lines represent the gating for tetramer-positive cells. Plots with shaded backgrounds indicate that after uncaging of the MHC, the peptide was found (by bead-based MHC stability assay and ELISA) to be unable to rescue degradation of the complex.