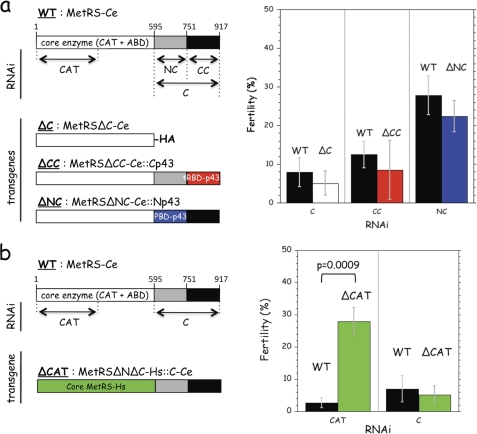
FIGURE 7.
Complementation of MetRS-Ce by a chimeric human MetRS. a, domain organization of MetRS-Ce. The core enzyme is made of the catalytic (CAT) and anticodon-binding (ABD) domains. The mRNA regions targeted by the CAT-, C-, NC-, and CC-RNAi are indicated. Three transgenes containing core MetRS-Ce were assayed for their ability to rescue inactivation of endogenous MetRS-Ce. They expressed a C-terminal truncated derivative of MetRS-Ce (MetRSΔC-Ce, with a C-terminal HA tag), and derivatives with the replacement of the CC- or NC-domains of MetRS-Ce by the C-terminal tRBD of human p43 (red, 57% identities with the CC-domain of MetRS-Ce) (MetRSΔCC-Ce::Cp43), or the N-terminal PBD of human p43 (blue, 17% identities with the NC-domain of MetRS-Ce) (MetRSΔNC-Ce::Np43). The fertility of wild-type (WT) and transgenic C. elegans strains expressing MetRSΔC-Ce (ΔC), MetRSΔCC-Ce::Cp43 (ΔCC), or MetRSΔNC-Ce::Np43 (ΔNC) was assessed after L1 feeding with the RNAi indicated. For each RNAi tested, fertility is expressed as the percentage of eggs laid per adult treated with that RNAi as compared with the number of eggs laid per untreated adult. b, a transgene containing the entire C-domain of MetRS-Ce was assayed for its ability to rescue inactivation of endogenous MetRS-Ce. The core domain of MetRS-Ce was replaced by the core domain of human MetRS (green, 55% identities with the core domain of MetRS-Ce) (MetRSΔNΔC-Hs::C-Ce). The fertility of wild-type (WT) and the transgenic strain expressing MetRSΔNΔC-Hs::C-Ce (ΔCAT) was assessed after L1 feeding with the RNAi indicated. For each RNAi tested, results are expressed as the percentage of eggs laid per adult treated with RNAi as compared with the number of eggs laid per untreated adult. Results shown are the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. Approximately 20 worms were tested for each trial. To assess the significance of the rescue of MetRS-Ce by MetRSΔNΔC-Hs::C-Ce in the presence of CAT-RNAi a two-tailed t test was performed.