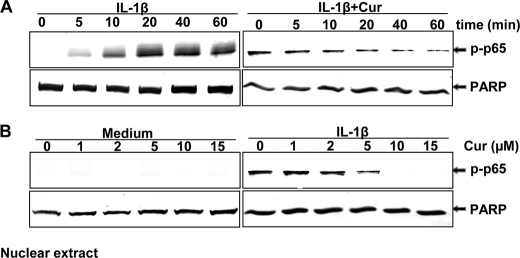
FIGURE 4.
Curcumin suppression of IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation. A, serum-starved human tenocytes (1 × 106 cells/ml) were either stimulated with 10 ng/ml of IL-1β for the indicated times or preincubated with 5 μm curcumin for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 60 min, co-treated with 10 ng/ml of IL-1β for 30 min, and then probed for phospho-p65 by Western blot analysis using antibodies to phospho-specific p65 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) (control). B, serum-starved human tenocytes were either incubated with curcumin at various concentrations (0, 1, 2, 5, 10, and 15 μm) for 4 h or preincubated with curcumin at various concentrations for 4 h followed by 10 ng/ml of IL-1β stimulation for 30 min. The nuclear extracts (500 ng of protein/lane) were probed for phospho-p65 by Western blot analysis using antibodies to phospho-specific p65 and PARP (control). Expression of PARP remained unaffected in the nuclear extracts. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments.