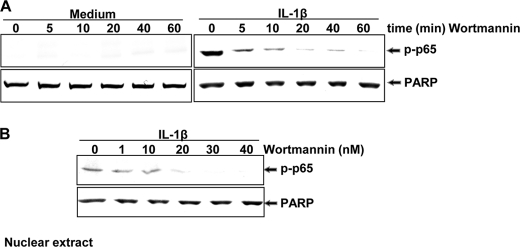
FIGURE 5.
Effect of wortmannin on IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation. A, serum-starved human tenocytes (1 × 106 cells/ml) were either stimulated with 20 nm wortmannin for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 60 min or preincubated with 20 nm wortmannin for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 60 min, co-treated with 10 ng/ml of IL-1β for 30 min, and then probed for phospho-p65 by Western blotting using antibodies to phospho-specific p65 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) (control). B, serum-starved tenocytes were preincubated with wortmannin at various concentrations (0, 1, 10, 20, 30, and 40 nm) for 1 h followed by 10 ng/ml of IL-1β stimulation for 30 min. Nuclear extracts (500 ng of protein/lane) were probed for phospho-p65 by Western blotting using antibodies to phospho-specific p65 and PARP (control). Expression of PARP remained unaffected in nuclear extracts. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments.