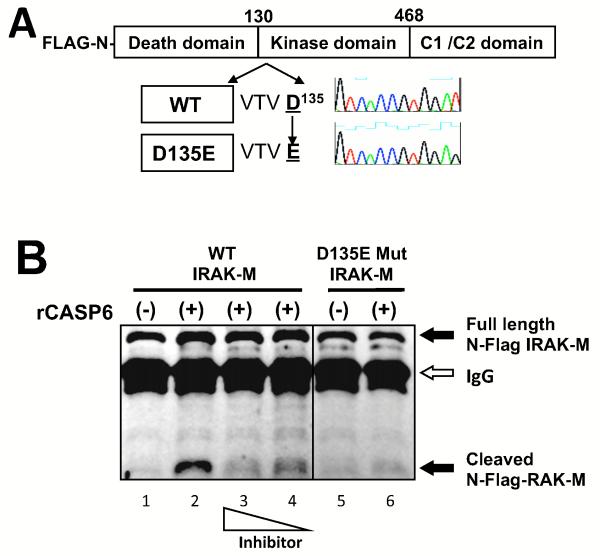
Figure 3. Active recombinant CASP-6 cleaves wild type but not mutant IRAK-M in vitro.
(A) Schema of IRAK-M (WT) and its CASP-6-target motif VTVD135 (D135E) mutant. Mammalian expression vectors of N-terminal FLAG tagged wild type were constructed by site-directed mutagenesis. (B) Western blot probed with anti-FLAG antibody. WT and mutant N-terminal flag-tagged IRAK-M were produced in 293T cells and isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. Immunoprecipitants were incubated in the absence (−) or the presence (+) of 1U active recombinant CASP-6 (rCASP-6) and cleavage was assayed by western blot. Full length 68 kD IRAK-M or N-terminal fragment are shown by arrow respectively. The signal from IgG heavy chain used in the IP is also shown by an arrow. The casapse inhibitor Z-VEID-FMK was added with rCASP-6 at concentrations 10 or 5 μg/ml (lane 3 and 4). CASP-6-target motif VTVD135 (D135E) mutant was applied to in vitro cleavage assay (lane 5 and 6). Black lines indicated that intervening lanes have been spliced out. All experiments were performed at least three times.