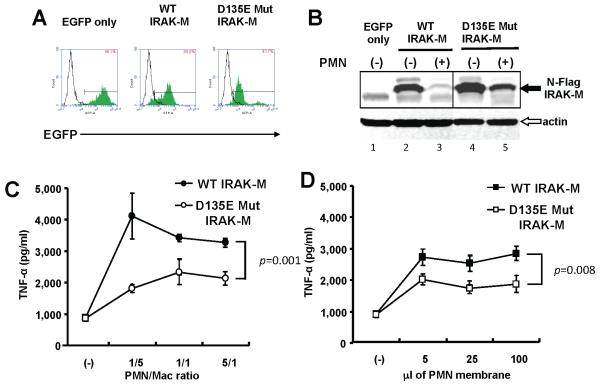
Figure 5. IRAK-M mutants are resistant to PMN-contact dependent cleavage in stably transfected THP-1 macrophages.
(A) FACS of THP-1 cells stably expressing wild type (WT) or mutant (D135E) IRAK-M. C-terminus HA-tagged IRAK-M pseudotyped lentivirual expression vector transduced THP-1 cells. The expression vector produced a polycystronic mRNA that contains IRAK-M, an IRES and EGFP coding sequence and allowing isolation of transduced cells by sorting. The number in the square indicates positive ratio of EGFP in each transfectant (green histograms) compared to parental cells (open histograms). (B) Western blot probed with anti-HA antibody. THP-1 macrophages expressing WT or mutant (D135E) IRAK-M were co-cultured with equal numbers of PMN for 2hr. An anti-β-actin antibody served as loading control. (C) TNF-α expression in cell culture supernatants quantified by ELISA. THP-1 macrophages expressing WT or mutant (D135E) IRAK-M were co-cultured with PMN for 2hr. The ratio of PMN to macrophages is shown on the x axis. P value for the difference in TNF-α expression is shown. (D) TNF-α expression in cell culture supernatants. THP-1 macrophages expressing WT or mutant (D135E) IRAK-M were stimulated with PMN membranes for 2hr. The volume of isolated membrane fractions is shown on the x axis. Representative data of three independent experiments are shown.