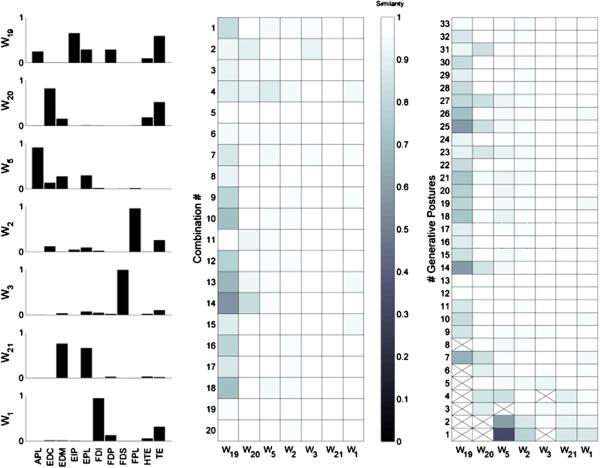
Figure 9.
The estimated synergies for one subject (bar plots, left column), and their robustness (similarity matrices, middle and right column). Synergies are numbered to match those in figure 10. Robustness (i.e. similarity) was assessed across the 20 different randomly selected combinations of generative postures (middle column), and quantified using the normalized dot product (NDP), which ranged from 0 (no similarity black) to 1 (perfect similarity, white). All robustness values were significantly greater than expected by random chance (0.14 ± 0.11). Synergy robustness was also assessed relative to changing the number of generative postures k (right column). Increasing k did not largely alter the structure of the existing synergies. A cross means that the synergy did not match another synergy in that compared set above random chance.