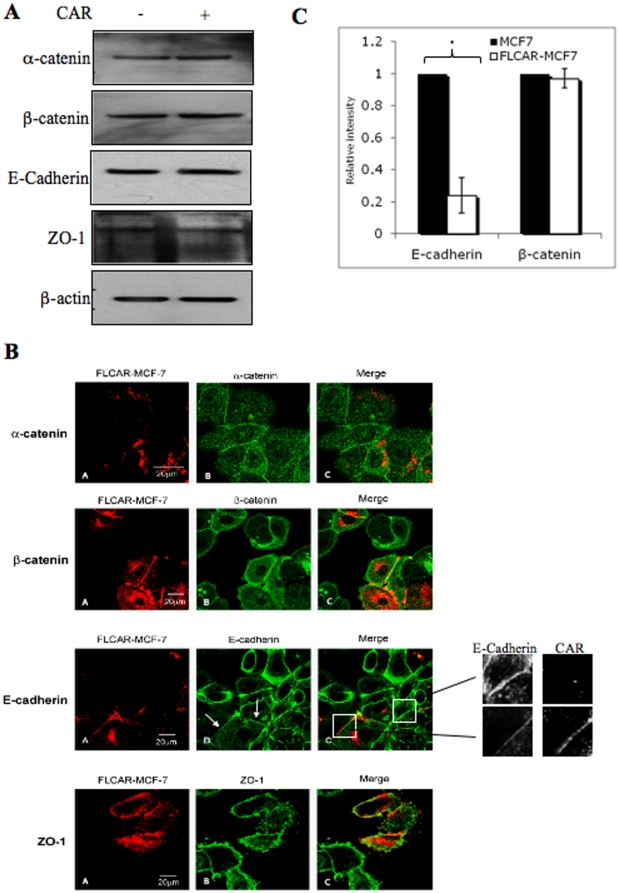
Figure 1. CAR reduces E-cadherin expression at CAR-expressing MCF7 cell junctions.
(A) MCF7 parental (−) or FLCARMCF7 (+) cell lysates subjected to western blot analysis for total α-catenin, β-catenin, E-cadherin and ZO-1 protein levels. Actin serves as a loading control. There was no difference in the level of expression of these proteins in the presence/absence of CAR. (B) Confocal images of MCF7 and FLCARMCF7 (red channel) cells immunostained for α-catenin, β-catenin, E-cadherin and ZO-1 antibodies labelled with Oregon green. The levels and localisation of α-catenin, β-catenin and ZO1 appeared the same in MCF7 and FLCARMCF7 cells but E-cadherin expression was reduced in CAR expressing junctions (denoted by white arrows and highlighted in the inset). These are representative images from at least 3 experiments, with reduced E-cadherin being evident in more than 80% of CAR expressing junctions. (C) Bar charts are quantitations of E-cadherin or β-catenin intensity at junctions between FLCARRFP positive cells (FLCARMCF7), or those without CAR (MCF7) and calibrated on a per pixel basis to correct for any differences in junction size/area. MCF7 junction intensity values were normalised to 1 and all values for FLCARMCF7 junctions represented as a relative value to this. Values were pooled from multiple cells and images (n = >25 junctions per condition) over three independent experiments and represented as relative mean intensity * P<0.05. Significance was determined by a two-way anova.