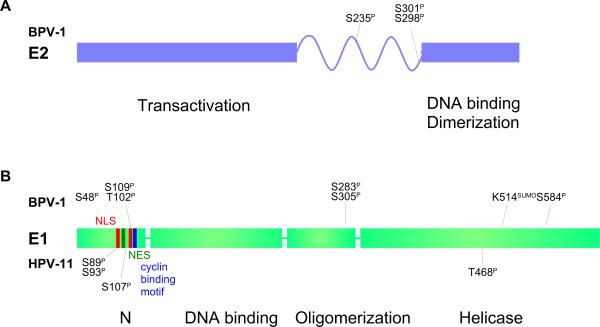
Figure 3. Domain structure of the E1 and E2 proteins.
A. The full-length E2 proteins of all papillomaviruses consist of two conserved domains linked by a less conserved hinge region. The N-terminal domain is important for transcriptional regulation and interaction with the E1 protein. The C-ternminal domain is a specific DNA binding and dimerization domain. Phosphorylation sites mapped in BPV-1 E2 are indicated (Lehman and Botchan, 1998; McBride et al, 1989).
B. The E1 proteins consist of four domains. The N-terminal domain is important for intracellular localization and contains both nuclear localization signals (NLS) and nuclear export signals (NES). The next domain is an origin specific DNA binding domain, followed by an oligomerization domain. The C-terminal domain contains the helicase function. Phosphorylation sites mapped in BPV-1 are indicated above and those mapped in HPV11 are indicated below. See text for references.