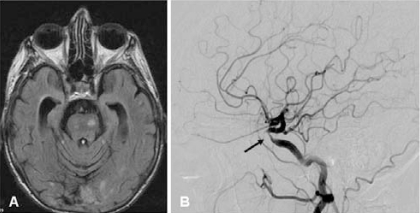
Fig. (5A).
Multiple infarcts in the cerebral pons, cerebellum, and occipital lobes in a patient with biopsy-proven giant-cell arteritis who developed ataxia and cognitive impairment after the initiation of glucocorticoid therapy. B) Cerebral angiography displaying carotid siphon stenosis in a patient with biopsy-proven giant-cell arteritis who developed recurrent transient ischemic attacks (aphasia and hemiparesis) in spite of high-dose glucocorticoids, antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy. This lesion was successfully treated with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (57).