Fig. 1. Genetic architecture of asthma and allergic diseases.
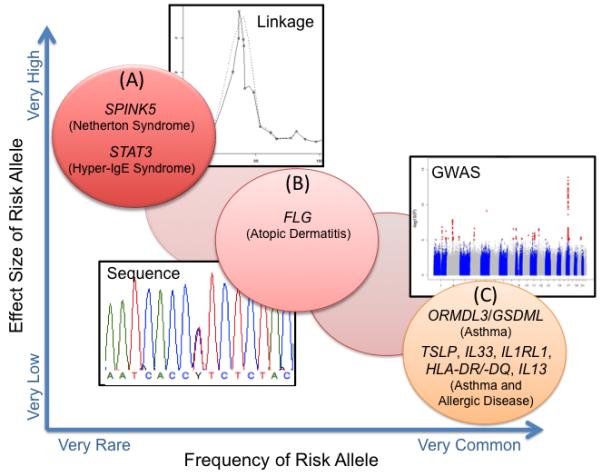
Examples are shown for (A) Monogenic diseases with allergic phenotypes that are caused by highly penetrant rare (<1%) mutations. These disease genes can be discovered by linkage studies in families segregating the disease. (B) Complex diseases or phenotypes with low frequency (1-5%) risk alleles with intermediate effect sizes. The relative paucity of genes in his category reflects the limited ability for re-sequencing studies in the past. (C) Complex diseases and phenotypes with common disease risk alleles (>5%) with very low effect sizes and penetrances can be discovered by GWAS. Modified from references (179, 183).
