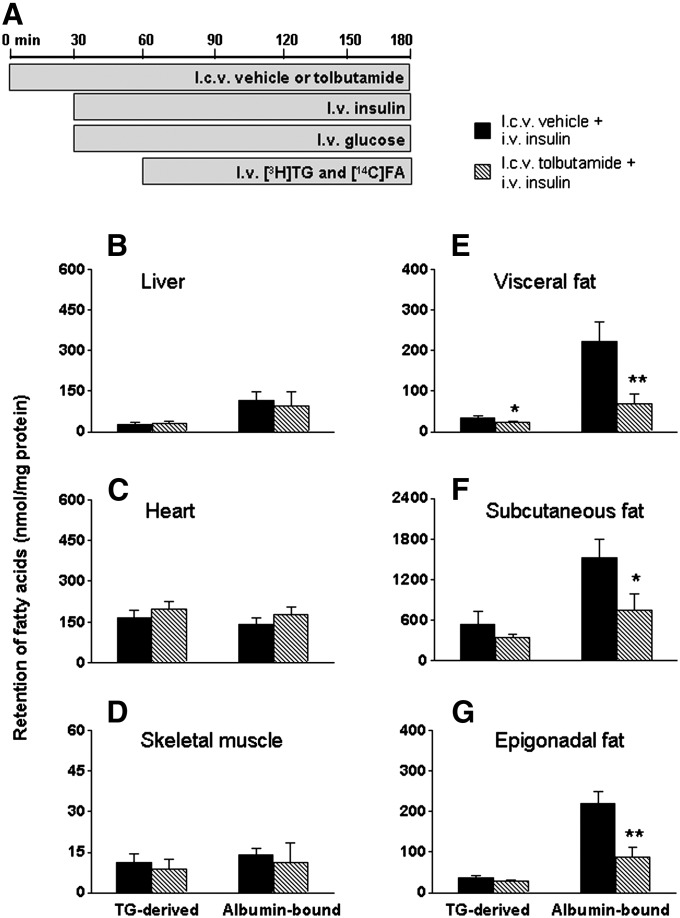
Fig. 4.
ICV administration of tolbutamide impairs the stimulation of FA retention in WAT induced by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp conditions. Postabsorptive, body weight-matched mice received continuous ICV infusion of vehicle (black bars) or tolbutamide (12 nmol/h, hatched bars) 30 min before the start of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp study (A). Infusion of glycerol tri[3H]oleate within VLDL-like emulsion particles and albumin-bound [14C]oleic acid was started 30 min after the start of the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp study and maintained for 2 h. Subsequently, the mice were euthanized, and the retention of TG-derived FA and albumin-bound FA was determined in liver (B), heart (C), skeletal muscle (D), visceral fat (E), subcutaneous fat (F), and epigonadal fat (G). Values are means ± SEM for at least five mice per group. *P < 0.05 versus vehicle, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle.