Figure 6.
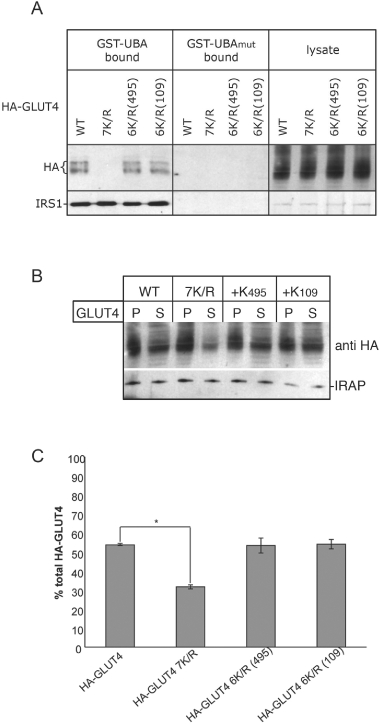
Further characterization of 6K/R mutant versions of HA-GLUT4. Cell lysates prepared from 3T3-L1 adipocytes expressing either wild-type HA-GLUT4, HA-G4-7K/R (7K/R), HA-G4-6K/R+K495 [6K/R(495)] or HA-G4-6K/R+K109 [6K/R(109)] were (A) incubated either GST–UBA or GST–UBAmut immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose as in Figure 3 with the immunoblot being probed for HA to detect the GLUT4 constructs and an antibody that specifically recognizes IRS1 as a positive control, or (B) subjected to 16 000 ×g centrifugation for 20 min (as in Figure 4B). The amount of the HA-tagged versions of GLUT4 and IRAP in the pellet (P) and supernatant (S) was determined by immunoblot analysis. (C) Partitioning of HA-GLUT4 (wild-type and mutants thereof, as above) between pellet and supernatant fractions shown in (B) was compared using image analysis software (ImageJ, NIH) to quantify the optical density of the bands on the blot. The percentage of total HA-GLUT4 in the supernatant fraction is plotted. n = 3, *statistically significant difference (p < 0.001, unpaired Student's t-test). Error bars ± standard error of the mean.
