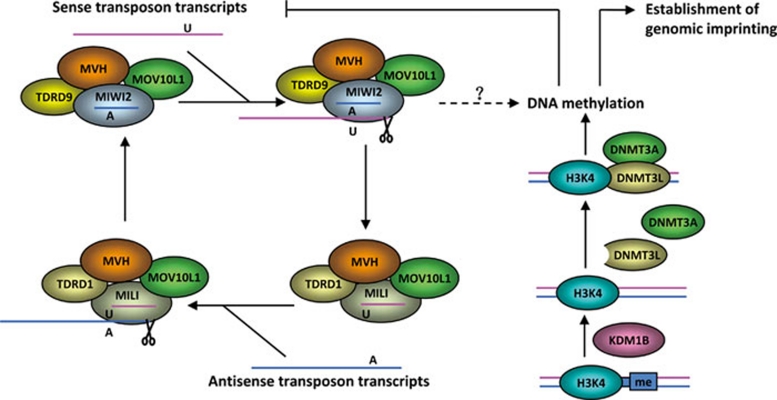
Figure 2.
De novo DNA methylation in the mammalian germline. Two Piwi proteins, MILI and MIWI2, are required for piRNA (Piwi-interacting RNA) generation. The piRNAs are generated in fetal male gonads, and play important roles in silencing transposons by causing DNA methylation. The primary piRNAs are bound with cytoplasmic MILI, which cleaves antisense transposon transcripts. The secondary piRNAs are bound with MIWI2, which cleaves sense transposon transcripts. The sense transposon transcripts produce primary piRNAs with 5′ uridine (U), whereas antisense transposon transcripts produce secondary piRNAs with an adenine (A) at position 10. Generation of piRNAs also require Tudor domain-containing (TDRD) proteins, mouse VASA homolog (MVH), and putative DExD-box helicase MOV10L1. The interaction between Piwi proteins and TDRD proteins is essential for generation of piRNAs. TDRD9-MIWI2 and TDRD1-MILI are two conserved complexes that generate primary piRNAs and secondary piRNAs, respectively. MVH and MOV10L1 are required for the activity of both MILI and MIWI2 in piRNA generation and de novo DNA methylation. DNMT3L interacts with unmethylated H3K4, and recruits DNMT3A to specific genomic regions for DNA methylation. The histone H3K4 demethylase KDM1B catalyzes demethylation of H3K4, by which it promotes de novo DNA methylation.