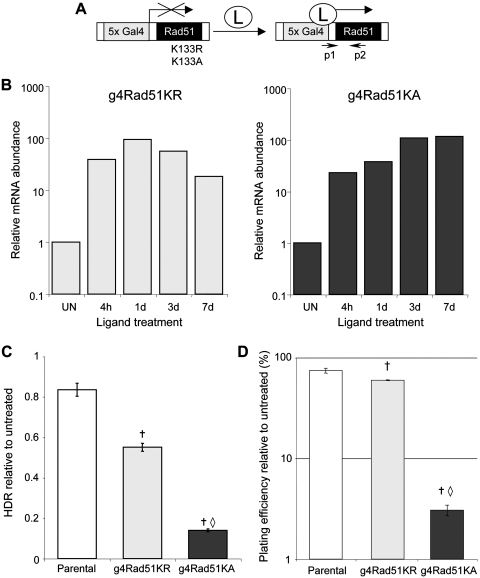
Figure 3.
Inducible expression of two dominant-negative Rad51 mutants cause different degrees of HDR disruption. (A) Diagram shows inducible expression cassettes for Rad51-K133R and Rad51-K133A, in which transcription from the g4 promoter requires addition of the cell-permeable Genostat ligand (L). Primers p1 and p2 are used for genotyping and quantitative RT–PCR analysis. (B) mRNA abundance from the g4Rad51 expression cassettes, measured by quantitative RT–PCR, for the g4Rad51KR and g4Rad51KA cell lines after L-treatment for the times shown (h: hours, d: days), relative to untreated (UN). (C) Inducible Rad51-K133R and Rad51-K133A expression causes mild and severe HDR disruption, respectively. Shown is repair by HDR in the presence of L, relative to untreated, using the DR-GFP reporter integrated into the parental, g4Rad51KR and Rad51KA cell lines. (D) The degree of HDR disruption is commensurate with the effect on viability. Shown is the clonogenic survival of the cell lines in C, after continuous L-treatment. Dagger denotes a difference in frequency compared to parental cells (P < 0.0002). Open diamond denotes a difference of g4Rad51KA cells compared to g4Rad51KR cells (P < 0.0001).