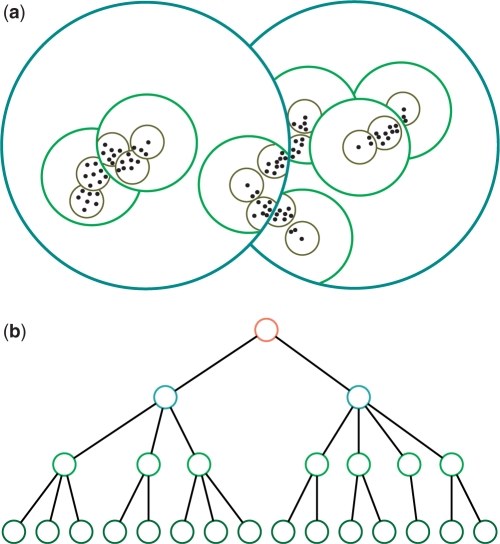
Figure 1.
PBP tree. A PBP tree partitions an input space into a set of non-overlapped hyperspherical regions at various distance levels indicated by circles with different colors (a), and organizes input sequences in a tree-like hierarchical structure (b). Each point in (a) represents a sequence, and the color of a node in (b) corresponds to the color of a circle in (a). For ease of presentation, the leaf nodes are omitted, and a root node is created that includes all descendent nodes. The partition, though not necessarily reflecting the true structure of a data set as shown in (a), can significantly accelerate a clustering process by removing most unnecessary sequence alignment operations and distance computation.