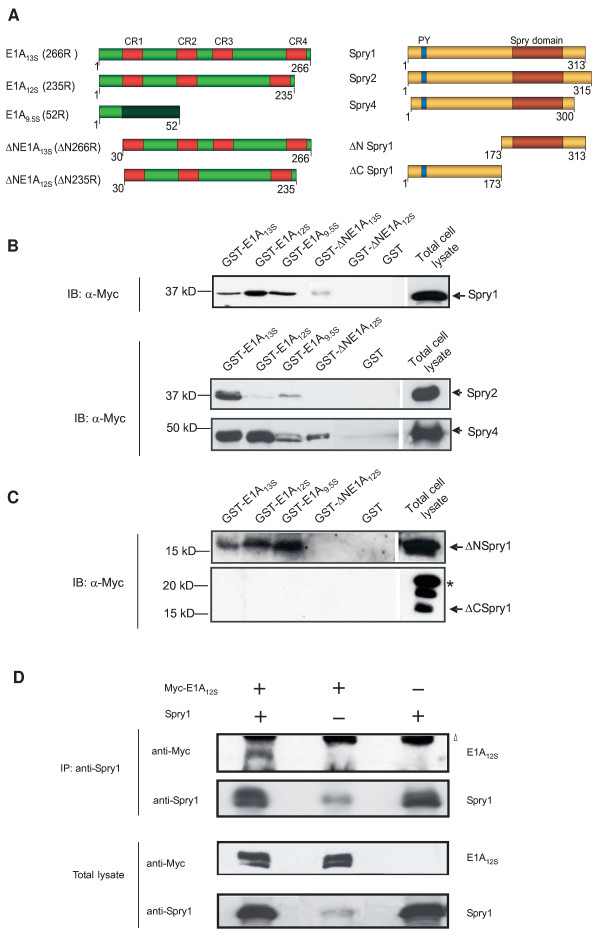
Figure 1.
Sprouty proteins interact with E1A isoforms. (A) Schematic representation of the E1A wild type isoforms E1A13S, E1A12S, E1A9.5S, the deletion mutants ΔNE1A13S and ΔNE1A12S (with a deletion of the first 29 N-terminal amino acids) and Spry isoforms and deletion mutants (ΔNSpry1 with a deletion of amino acids 1-173; ΔCSpry1 with a deletion of amino acids 174-313). Red boxes in E1A proteins represent the conserved regions 1 to 4; the brown box in Spry represents the Spry domain and the blue box the conserved tyrosine phosphorylation site. (B, C) For GST pull-down assays HeLa cell extract, containing the isoform Spry1, Spry2 or Spry4 (B) or the Spry-mutants ΔNSpry1 or ΔCSpry1 (C) were incubated with the protein leader sequence GST- or GST-E1A-fusion proteins as indicated. 0.5 mg of cellular lysate and 40 μg of GST-E1A or GST were incubated at 4°C for 1 h. Proteins bound were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and immunoblot analysis was performed with antibodies directed against the Myc-epitope of Spry-fusion proteins. * The higher molecular weight band may represent post-translational modification of Spry1 (palmitoylation and phosphorylation) as reported before [22]. (D) For immunoprecipitation HeLa cells were transiently co-transfected with Spry1 and Myc-tagged E1A12S expression vectors as indicated. Cell extracts were prepared 48 h post transfection and incubated with anti-Spry1 antibodies. Interacting proteins were precipitated and analyzed on SDS-PAGE by Western blotting using anti-Spry1 and anti-Myc antibodies. Transient expression was examined in the total lysate (Δ co-eluted antibody heavy chains).