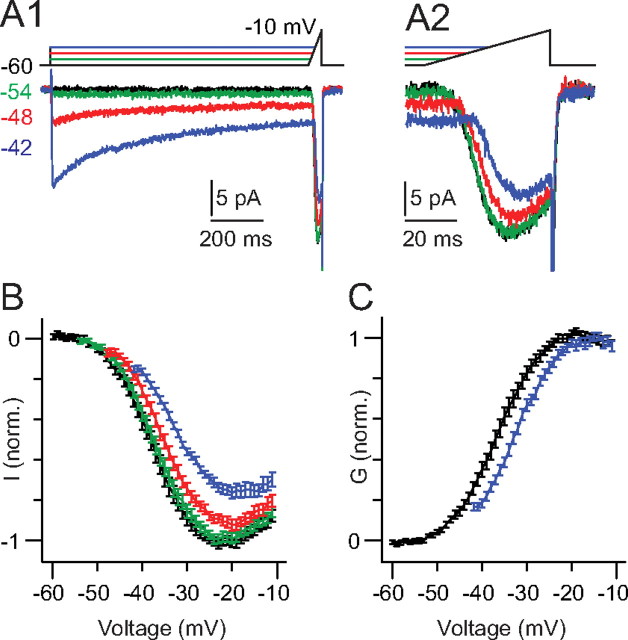
Figure 3.
Presynaptic Ca currents inactivate at depolarized membrane potentials in the physiological range. A1, The RB was stepped to potentials between −60 and −42 mV for 750 ms. Then, the membrane potential was ramped at 1 mV/ms to −10 mV. A2, The maximal Ca current is reduced by inactivation. B, Summary data from n = 16 RBs illustrate the reduction in maximal current (to ∼75% of control) induced by inactivation. C, Comparison of the conductance–voltage relationships recorded following prepulses to −60 (no prepulse) or −42 mV illustrates a small rightward shift in half-maximal activation potential (from −37.1 to −33.4 mV as determined by a Boltzmann sigmoid fit to the averaged data) that accompanies inactivation.