Figure 5.
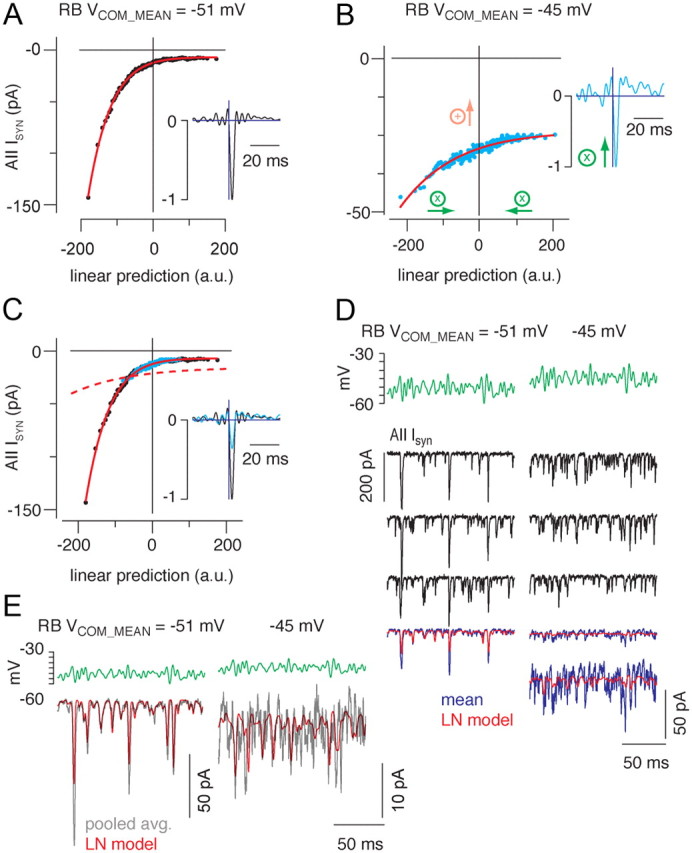
Depolarizing the rod bipolar cell membrane potential reduced synaptic gain. A, B, The static nonlinearity and linear filter (insets) are shown for conditions in which the mean rod bipolar command potential (Vcom_mean) was either −51 (A) or −45 mV (B); in both cases, the SD of the white noise input was 3 mV. The nonlinearities were fit (red line) simultaneously by allowing a scale factor to differ between conditions. C, The nonlinearity of the depolarized mean condition could be aligned with the nonlinearity of the hyperpolarized mean condition by adding a constant (9.3 pA for this recording and 5.5 ± 2.4 pA for n = 5 paired recordings; B, orange arrow) and scaling the x-axis (by 0.36 for this recording and 0.32 ± 0.04 for n = 5 paired recordings; B, green arrows). To maintain a constant L-N model output, the filter was multiplied by the same scaling factor (inset). Depolarizing the RB reduced output gain to 36% of the gain in the hyperpolarized condition (32 ± 4% for the population of n = 5 paired recordings). The red dashed line shows the unscaled fit in the depolarized condition in B. Depolarizing the RB reduced synaptic gain. D, Three responses to repeated stimuli with means of −51 mV (left) and −45 mV (right) illustrate the variability inherent in the data. The L-N prediction is better correlated with the averaged response at −51 mV than with the averaged response at −45 mV because of the increased amount of uncorrelated release at depolarized potentials as well as the reduction in the size of the responses correlated with the stimulus. The average response in the −45 mV condition is shown both at the same scale as the −51 mV condition and on an expanded scale. E, Pooling data from n = 5 recorded pairs improves the predictive power of the L-N model. Gray trace, Response to repeated stimulus averaged across all recorded pairs; red trace, L-N prediction derived from model constructed with pooled data. r2 = 0.86 and 0.72 for −51 and −45 mV, respectively.
