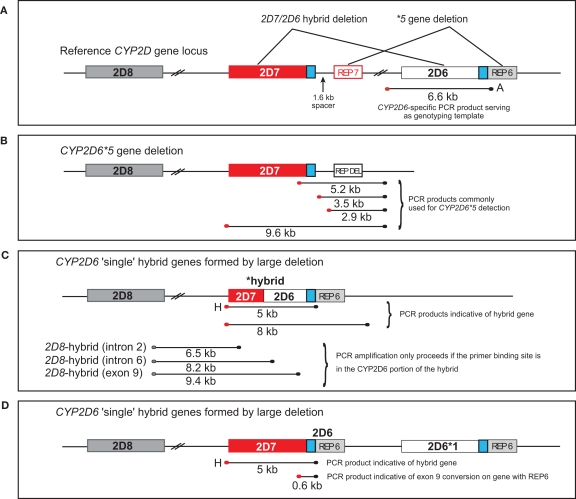
Figure 1.
Overview of the CYP2D7/2D6 hybrid genes. CYP2D6, CYP2D7, and CYP2D8 genes are shown in light gray, red, and dark gray boxes, respectively. The 600-bp repeat element immediately downstream of exon 9 is shown in blue. CYP2D6 and CYP2D7-derived repetitive elements (REP) are in red and light gray; REP-DEL indicates a fused repeat element generated by a large deletion involving parts of those elements from both genes. PCR fragments generated are represented as lines and their sizes are given in kilobyte. Red and black endpoints denote primer specificity to CYP2D6 and CYP2D7. (A) Graph represents the CYP2D reference locus. Areas affected by large deletions and implicated in CYP2D7/2D6 hybrid formation and the CYP2D6*5 gene deletion are as indicated. (B) Graphic display of the CYP2D6*5 gene deletion allele. XL-PCR amplicons utilized for detection are shown. (C) Graphic display of CYP2D7/2D6 hybrid genes and their detection by amplification of fragment H. Other depicted fragments are only amplified, if respective rearrangements are present in a sample. (D) Representation of an allele with a CYP2D7 gene lacking the 1.6-kb spacer. This CYP2D7 variant also supports formation of fragment H although the CYP2D7/2D6 switch occurs in the downstream region.