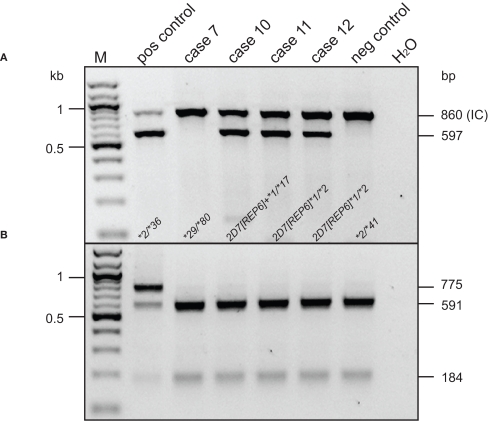
Figure 5.
Genotype analysis for CYP2D7 exon 9 conversion and CYP2D7[REP6]. M, 100-bp ladder. Cases, positive, and negative control DNAs and their respective genotypes are as indicated. Selected marker bands are given in kilobyte to the left; PCR product and restriction fragment lengths are shown to the right in base pair. The top panel (A) shows a duplex assay performed on genomic DNA that detects the CYP2D6 exon 9 conversion present in e.g., CYP2D6*36 and alleles carrying a CYP2D7[REP6]. The forward primer is specific for CYP2D7 exon 9 and the reverse primer for CYP2D6 binding to the REP6 junction (see Figure 1). A second primer pair served as internal control (IC). Samples positive for CYP2D6*36 or CYP2D7[REP6] produced a 597-bp long amplicon in addition to the 860-bp-long IC product. The bottom panel (B) shows a RFLP-based assay performed on the 6.6-kb long CYP2D6-specific genotyping template. Uncut PCR product (775 bp) is indicative of a CYP2D7 exon 9-derived sequence on a CYP2D6 background. The CYP2D6*2/*36 control DNA sample is positive for CYP2D7 exon 9 in both assays, while cases 10, 11 and 12 showed a CYP2D6-derived pattern in the RFLP assay (591 + 184 bp).