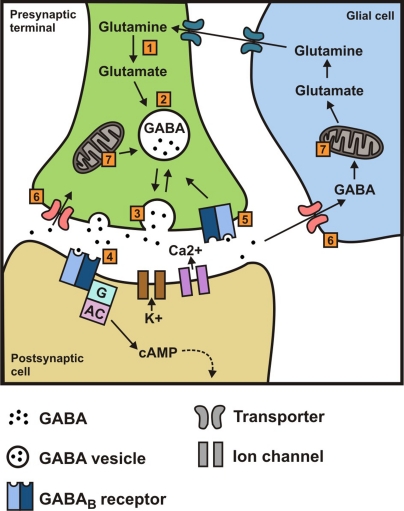
Figure 1.
(1) Synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from glutamine/glutamate (catalyzed by l-glutamate decarboxylase (GAD); (2) transport and storage of GABA; (3) release of GABA by exocytosis; (4) binding to GABAB receptors and subsequent downstream effects mediated via a G protein and/or cAMP to K+ and Ca2+ channels; (5) binding to presynaptic receptors; (6) reuptake in presynaptic terminal and uptake by glia; (7) transamination of GABA to α-ketoglutarate (catalyzed by GABA transaminase, GABA-T), thereby regenerating glutamate and glutamine; glial glutamine then re-enters the neuron.