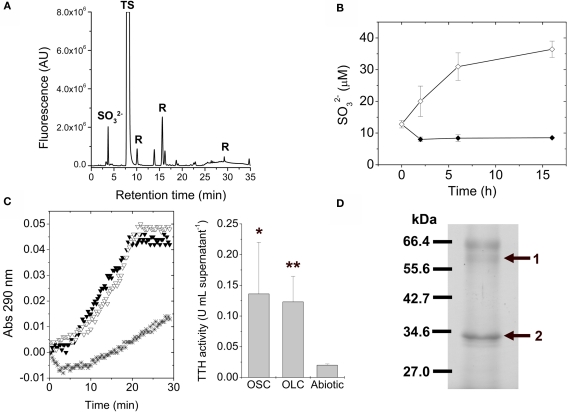
Figure 6.
Tetrathionate hydrolase activity is present in A. ferrooxidans culture supernatants. (A) Identification of low molecular weight thiols in A. ferrooxidans culture supernatants by HPLC. Thiols present in the culture supernatants from A. ferrooxidans subjected to 5 h OLC-incubation were derivatized with the monobromobimane reagent and separated by using HPLC. sulfite; TS, thiosulfate; R, reagent or water-derived peaks. (B) Changes in sulfite concentrations in thiosulfate-grown A. ferrooxidans culture supernatants during OSC- (♦) or OLC- (⋄) incubations. Aliquots were taken from cultures at the indicated times, derivatized with monobromobimane reagent, and analyzed by HPLC. Sulfite concentrations were determined by integration of the area corresponding to the sulfite peak on each chromatogram. (C) (Left panel) Cells were separated from their growth medium by centrifugation and the filtered supernatants were used directly for TTH activity measurements. Spectrophotometer original traces [(A), 290 nm] from representative continuous TTH activity assays of supernatants from thiosulfate-grown A. ferrooxidans cultures subjected to 16 h OSC-(▼) or OLC-(∇) incubations. The Abiotic control (*) corresponds to the tetrathionate-dependent increase in absorbance at 290 nm when sterile DSMZ 71 medium (without thiosulfate) was used instead of culture supernatants in the TTH assay. (Center panel), TTH activity (expressed as U mL supernatant−1) from A. ferrooxidans culture supernatants. Statistically significative differences (Student's t-test; n = 3; *, p value < 0.05; **, p value < 0.005) are indicated. (D) Identification of TetH protein in supernatants from A. ferrooxidans cultures incubated under OLC. Proteins precipitated by the PRMM method were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue G-250. The bands obtained were isolated from the gel and identified by mass spectrometry analysis. The protein band corresponding to the tetH gene product is indicated by an arrow.