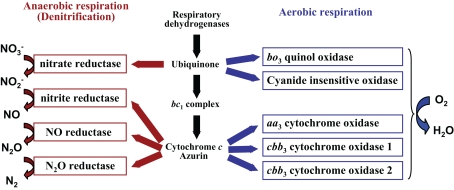
Figure 1.
Branched respiratory chain of P. aeruginosa. Under aerobic conditions, oxygen is utilized as a terminal electron acceptor and reduced to water by five terminal oxidases. Two quinol oxidases, the bo3 oxidase and the cyanide-insensitive oxidase, receive electrons directly from quinol. Three cytochrome c oxidases, the aa3 oxidase and the two cbb3 oxidases, receive electrons via the cytochrome bc1 complex and c-type cytochromes or a small blue-copper protein azurin. Under anaerobic conditions, electrons are transferred to nitrogen oxides via the denitrification enzymes.