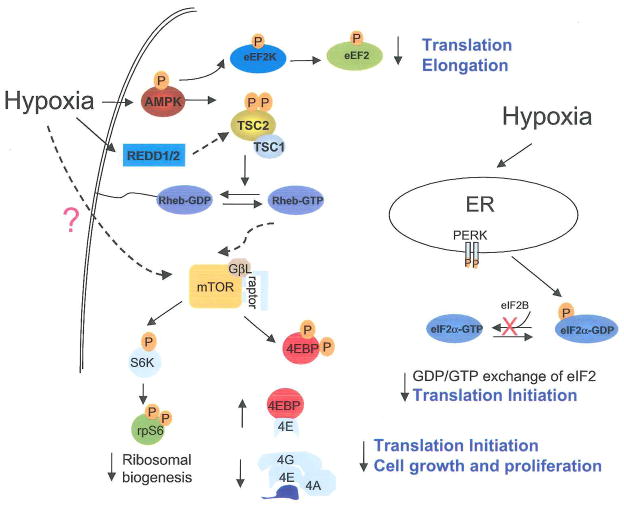
Figure 7. Schematic diagram for the signaling pathways modulated by low O2 that lead to translational inhibition.
Hypoxia suppresses signaling for translation initiation, elongation, and ribosome biogenesis via concomitant inhibition of eIF2α eEF2, and mTOR downstream targets 4EBP1, p70S6K, and rpS6. The mTOR regulation involves the AMPK/TSC2/Rheb pathway and is activated by hypoxia-induced decreases in cellular bioenergetics. The eIF2α phosphorylation may be trigged by ER-stress activated PERK and the eEF2 inhibition involves AMPK. HIF-inducible REDD1 has been implicated in the regulation of mTOR upstream of TSC2. Mutations of TSC2 in tumor cells greatly impede hypoxia-induced mTOR inhibition and G1 arrest. Thus, hypoxic translational control may ultimately affect cell growth and proliferation under low O2.