Fig. 2.
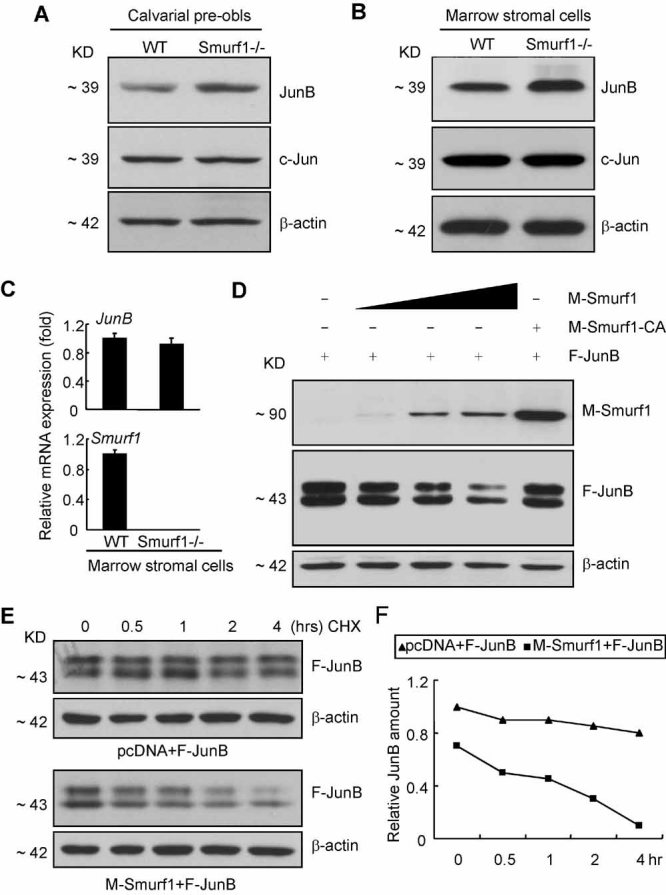
Smurf1 induces JunB degradation in vivo and in vitro. (A, B) JunB protein level was increased in the primary calvarial (A) and bone marrow stromal cells (B) of Smurf1−/− mice compared with that of wild-type mice (n = 4). c-Jun protein level also was determined by Western blot analysis. (C) Real-time qPCR data showed that JunB mRNA level underwent no significant changes in the bone marrow stromal cells of Smurf1−/− and wild-type mice (n = 3). (D) Smurf1 expression decreases JunB protein levels in a dose-dependent manner (n = 5). HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-JunB and Myc-Smurf1 plasmids. Myc-Smurf1 was added in different amounts. Myc-Smurf1 (C710A) is a mutated Smurf1 in which an active-site cysteine in its catalytic domain is converted into alanine to abolish its activity as an ubiquitin ligase. (E, F) HEK293T cells transfected with Myc-Smurf1 and Flag-JunB were treated with protein translation inhibitor cycloheximide (80 µg/mL) for indicated time and subjected to Western blot analysis of JunB protein levels to determine the half-life of JunB proteins in the presence or absence of Smurf1 overexpression in HEK293T cells (n = 3). Both Western blot (E) and its quantification (F) are shown.
