Fig. 3.
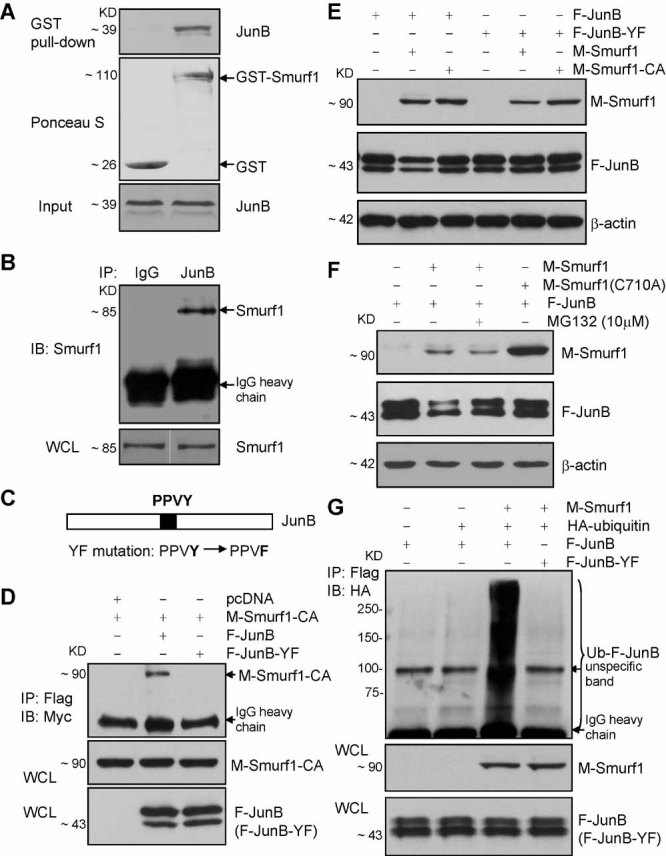
Smurf1 interacts with JunB through a PY motif and induces its ubiquitination and degradation. (A) GST-Smurf1 directly interacts with JunB protein. In vitro–translated JunB protein was copurified with GST-Smurf1 in a GST pull-down assay (n = 3). (B) JunB-Smurf1 interaction in mesenchymal C2C12 cells. Smurf1 was identified in the immunoprecipitates by anti-JunB antibodies (n = 3). (C) A diagram showing a YF mutation in the PY motif of JunB that was generated to examine if the PY motif is required by Smurf1-induced JunB degradation. (D) Wild-type JunB protein interacts with Smurf1, whereas JunB (YF) mutant cannot (n = 3). HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-Smurf1-C710A and Flag-JunB or Flag-JunB-YF. IP assays were carried out using anti-Flag antibodies, and immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot using anti-Myc antibodies; whole-cell lysates also were examined to ensure that both JunB and Smurf1 were expressed. (E) Smurf1 overexpression could not decrease the protein level of JunB-YF (n = 4). HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. (F) Proteasome inhibitor MG132 rescued JunB protein from Smurf1-induced degradation (n = 3). HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids as shown. Cells transfected with Myc-Smurf1 and Flag-JunB were treated with MG132 (10 µM) for 4 hours before being harvested and subjected to Western blot analysis. (G) JunB ubiquitination assay (n = 3). 293T cells transfected with HA-ubiquitin, Myc-Smurf1, and Flag-JunB or Flag-JunB-YF were treated with MG132 for 4 hours before harvesting, and polyubiquitinated JunB was immunoprecipitated by anti-Flag and immunoblotted with anti-HA.
