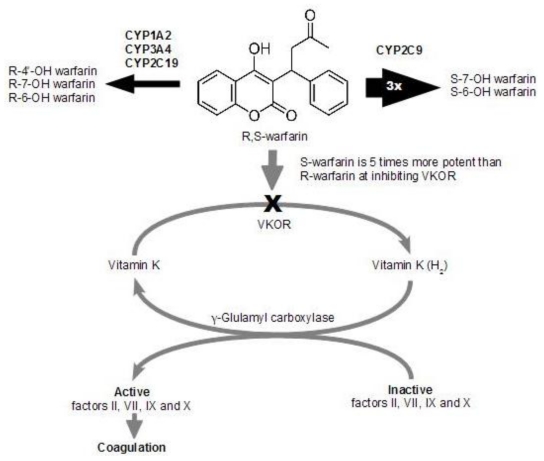
Figure 1.
Warfarin metabolism. (Warfarin is metabolized in the liver. CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP3A4 metabolize the (R)-enantiomer and CYP2C9 metabolizes the more potent (S)-enantiomer. Warfarin inhibits vitamin K reductase complex subunit 1 to interfere with the vitamin-K-dependent carboxylation of clotting factors prothrombin II, VII, IX, and X.).