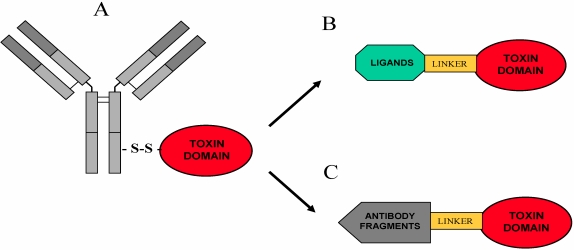
Figure 5.
From chemically-conjugated immunotoxins to recombinant fusions. Schematic representation of a classical immunotoxin (IT) in which a monoclonal antibody is joined via a disulfide bond to a toxin domain (A) and recombinant fusions between sequences coding for (B) ligands (such as growth factor domains, hormones, autocrine factors) or (C) antibody fragments (single-chain antibodies, Fab fragments or disulfide-stabilized Fv) link to the toxic moieties via different Linker peptides.