Fig. 4.
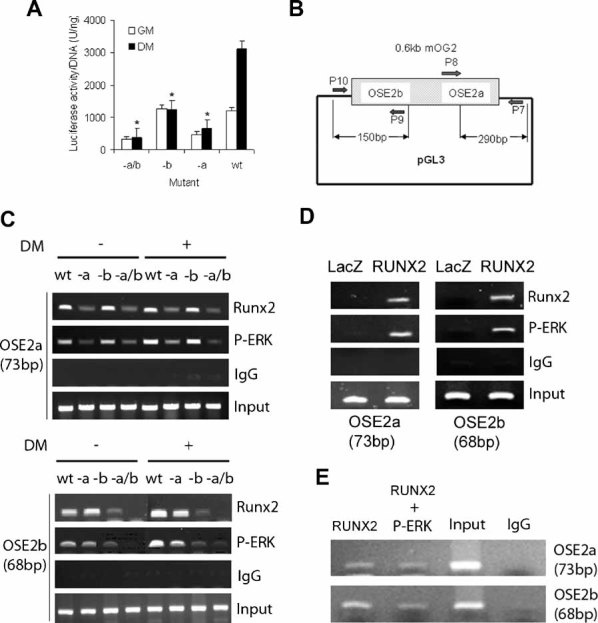
Association of P-ERK with mOG2 chromatin requires intact OSE2 regions and RUNX2. (A) Effect of OSE2 mutations on mOG2 promoter activity. To confirm that OSE2a and OSE2b are required for activation of Ocn, MC3T3-E1c4 cells were transfected with wild-type 0.6mOG2-luc (wt) or 0.6mOG2-luc harboring point mutations in OSE2a (–a), OSE2b (–b), or both sites (–a/b) and assayed for luciferase activity after growth in GM or DM for 6 days. The OSE2 mutant is significantly different from wild- type (DM samples only), p < .01(*). (B) Schematic showing location of PCR primers used for detecting interactions with OSE2a or OSE2b in WT or mutant 0.6mOG2-luc. (C) Mutation of OSE2 sites block binding of RUNX2 and P-ERK to mOG2 chromatin. Cells were transfected with WT or mutant 0.6mOG2-luc and cultured in GM or DM as in panel A. Isolated chromatin fragments were precipitated with anti-RUNX2 and anti-P-ERK antibodies or control IgG and ChIP DNA analyzed by PCR using the primers indicated. (D) Runx2 is indispensable for binding of P-ERK to mOG2 chromatin. C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal cells were transduced with control adenovirus (AdLacZ) or an adenovirus expressing Runx2 (AdRunx2) and grown for 4 days before chromatin isolation and ChIP analysis. Note the lack of a positive ChIP signal for P-ERK in the absence of RUNX2. (E) ChIP-re-ChIP detection of RUNX2 and P-ERK on Bglap2 chromatin. MC3T3-E1c4 cells were grown for 6 days as in panel A. ChIP was performed using anti-RUNX2 antibody. A portion of the immunoprecipitated chromatin complex was eluted from agarose beads and subjected to a second ChIP with either anti-P-ERK antibody or IgG. ChIP DNA then was analyzed using PCR primers specific to OSE2a and OSE2b (see Fig. 1A).
