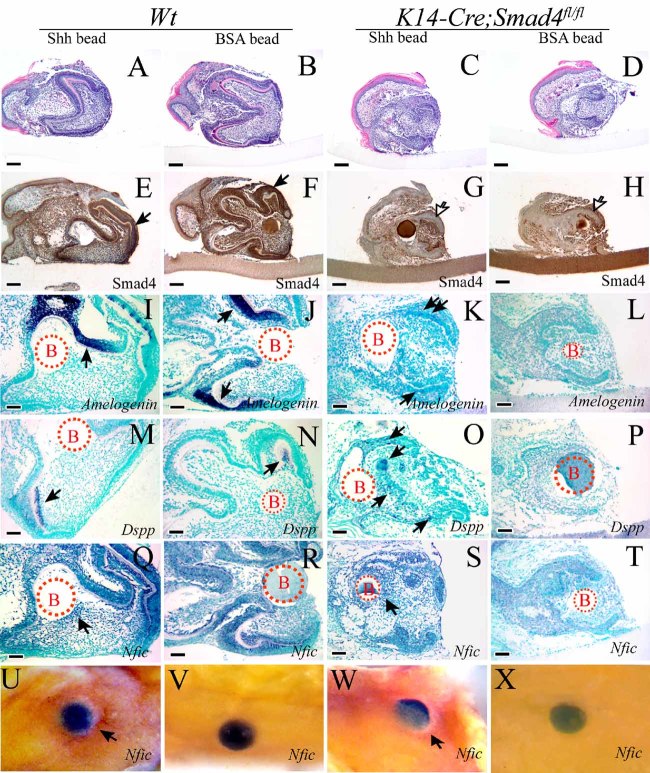
Fig. 7.
Rescue of Nfic gene expression by ectopic Shh in K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl mice. Analysis of gene expression in newborn wild-type (Wt) and K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl tooth germs cultured with Shh and BSA beads in dental pulp for 2 days. (A–D) H&E staining. (E–H) Immunohistochemistry with Smad4 antibody. Smad4 expression is not detectable in the dental epithelium of K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl tooth germs. (I–X) In situ hybridization of Amelogenin (I–L), Dspp (M-P), and Nfic (Q–X) of sections (I-T) and in whole mount (Nfic expression, U–X). Expression of Amelogenin and Dspp is clearly detectable in wild-type samples (I, J, M, N). Expression of Amelogenin and Dspp is not detectable in tooth germ of K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl mice treated with BSA beads (L, P) but is modestly detectable following treatment with Shh beads (K, O, arrows indicate positive signal). Nfic expression is detectable around the Shh beads in the dental pulp of both wild-type and K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl mice (Q, S, U, W, arrows indicate positive signal), whereas Nfic expression is undetectable in K14-Cre;Smad4fl/fl samples treated with BSA beads (T, X). Scale bars (A–H) = 100 µm; scale bars (I–T) = 50 µm.