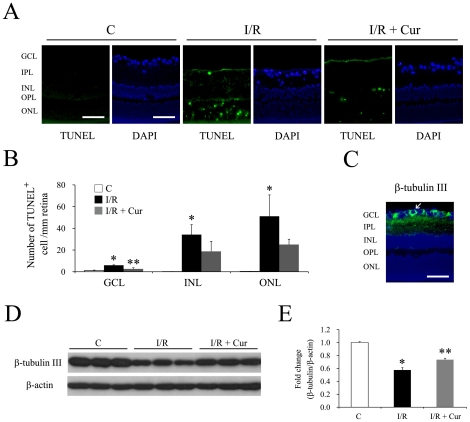
Figure 3. Curcumin inhibited I/R induced apoptotic cell death of retinal neurons and down-regulation of β-tubulin III.
(A) Representative pictures of TUNEL assay on the retina sections 2 days after the injury. A TUNEL-positive retinal ganglion cell is indicated with white arrowhead. Blue color: DAPI stained nuclei. Green color: TUNEL-positive cells. The scale bar represents 50 µm. (B) Quantitative results of TUNEL-positive cells in the GCL. (n = 4–5 different samples in each group, *P<0.01 compared with non-injured retinas; **P<0.05 compared with I/R-injured retinas) The error bars represent standard error of the mean. (C-E) Curcumin rescued retinal I/R-induced down-regulation of β-tubulin III 2 days after I/R injury. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of β-tubulin III on retinal sections. Blue color: DAPI stained nuclei. Green color: β-tubulin III staining. The scale bar represents 50 µm. Representative western blots of β-tubulin III and β-actin in retinas (D) along with densitometric quantitative results (E) (n = 4 different samples in each group, *P<0.05 compared with non-injured retinas; **P<0.05 compared with I/R-injured retinas). The error bars represent standard error of the mean. Group abbreviations are: C, non-injured eyes; I/R, I/R-injured eyes; I/R + Cur, I/R-injured eyes of animals treated with 0.05% curcumin 2 days before the injury.